Exploring the Differences: Cricut vs Laser Cutter
When it comes to crafting and manufacturing, choosing the right tool can make a world of difference. Two popular options for precision cutting are Cricut machines and laser cutters. Each has its own strengths and limitations, making them suitable for different types of projects. In this article, we’ll delve into the differences between these two tools, helping you decide which one might be the better fit for your needs.
What is a Cricut?
A Cricut is a digital cutting machine designed primarily for crafting and hobbyists. It uses interchangeable blades to cut through various materials like paper, cardstock, fabric, vinyl, and more. The machine works in conjunction with Cricut Design Space, a user-friendly software that allows users to create or import designs, adjust settings, and send instructions to the machine. Cricut machines are known for their ease of use and versatility, making them popular among crafters, educators, and small businesses.
The Cricut ecosystem is built around customizable projects, enabling users to create everything from personalized gifts to home decor. While it’s a powerful tool for creative expression, its capabilities are somewhat limited compared to industrial-grade equipment like laser cutters.
What is a Laser Cutter?
A laser cutter is a precision tool that uses a focused beam of light to cut or engrave materials. Unlike the Cricut, which relies on mechanical blades, laser cutters use heat to vaporize or melt through materials, resulting in clean and precise cuts. They are capable of working with a wide range of materials, including wood, acrylic, metal, glass, and more.
Laser cutters come in various sizes and power levels, from small desktop models for hobbyists to large industrial machines for manufacturing. One notable example is the option, which offers a compact and affordable solution for home use.
Key Differences Between Cricut and Laser Cutter
To better understand the differences between these two tools, let’s break down their key features:
1. Precision and Accuracy
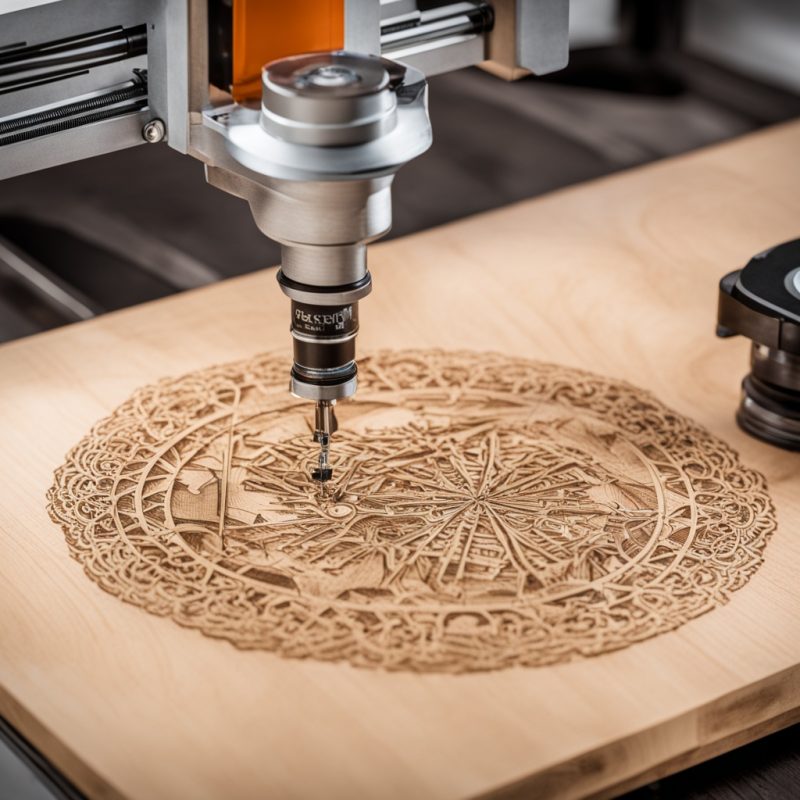
Laser cutters generally offer higher precision than Cricut machines. The laser beam is incredibly thin, allowing for intricate designs and tight corners. This makes laser cutters ideal for projects requiring extreme accuracy, such as circuit boards or fine metalwork. On the other hand, Cricut machines are limited by the width of their blades, which can make them less suitable for very detailed work.
2. **Material Compatibility
Cricut machines are designed to work with softer materials like paper, fabric, and vinyl. While they can handle some thicker materials (like cardboard or leather), they’re not equipped to cut through harder substances like metal or glass. Laser cutters, however, excel at cutting a wide variety of materials, including metals, plastics, woods, and composites. This makes them a more versatile choice for industrial and professional applications.
3. **Speed
Cricut machines are generally faster than laser cutters when working with their compatible materials. The mechanical cutting process is straightforward and doesn’t require preheating or setup time, making it ideal for quick projects. Laser cutters, while slower due to the heat-based cutting process, can often achieve higher precision and are better suited for bulk production runs.
4. **Cost
Cricut machines are typically more affordable than laser cutters, especially at the entry level. A basic Cricut machine might cost around $100–$200, while a decent desktop laser cutter could range from $500 to several thousand dollars. However, this cost difference can be offset over time by the versatility and durability of a laser cutter.
5. **Learning Curve
Cricut machines are known for their ease of use, with intuitive software and minimal setup required. Most users can start creating within minutes of unboxing. Laser cutters, on the other hand, often require more technical knowledge to operate safely and effectively. Users need to understand material settings, laser power levels, and safety precautions.
When to Choose a Cricut
If your projects involve soft materials like fabric, paper, or vinyl, and you’re looking for an easy-to-use solution with minimal setup, a Cricut might be the better choice. It’s ideal for:
- Personalized gifts and decorations
- Craft projects (e.g., scrapbooking, card-making)
- Small-scale signage and branding
- Educational purposes
The Cricut ecosystem also offers a wealth of pre-made designs and templates, making it a great choice for those who want to create without extensive design experience.
When to Choose a Laser Cutter
If your projects require precision cutting or involve harder materials like metal, glass, or thick wood, a laser cutter is likely the better option. It’s ideal for:
- Industrial manufacturing
- Fine woodworking and furniture making
- Metal fabrication and engraving
- Creative art projects (e.g., etching, glasswork)
Laser cutters also excel in scenarios where scalability is important. Once you’ve set up your design, a laser cutter can quickly produce multiple identical pieces with consistent quality.
Questions to Consider
Before making a decision, ask yourself the following questions:
- What materials am I working with? If it’s soft and thin, Cricut might suffice. For harder or thicker materials, a laser cutter is necessary.
- How detailed are my designs? Laser cutters handle intricate patterns better due to their higher precision.
- What’s my budget? Cricuts are more affordable upfront but may lack the versatility of laser cutters over time.
- Do I need a portable solution? Cricut machines are compact and easy to move, while laser cutters often require a dedicated workspace due to their size and power requirements.
Conclusion
Both Cricut machines and laser cutters have their place in the world of crafting and manufacturing. The Cricut is a fantastic choice for hobbyists and small-scale projects, offering ease of use and affordability. On the other hand, laser cutters provide unmatched precision and versatility, making them indispensable for professional and industrial applications.
If you’re exploring the debate, consider your specific needs and project requirements. By evaluating factors like material compatibility, precision, cost, and ease of use, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your goals.